High TCL1 levels are a marker of B-cell receptor pathway responsiveness and therapy resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Abstract:
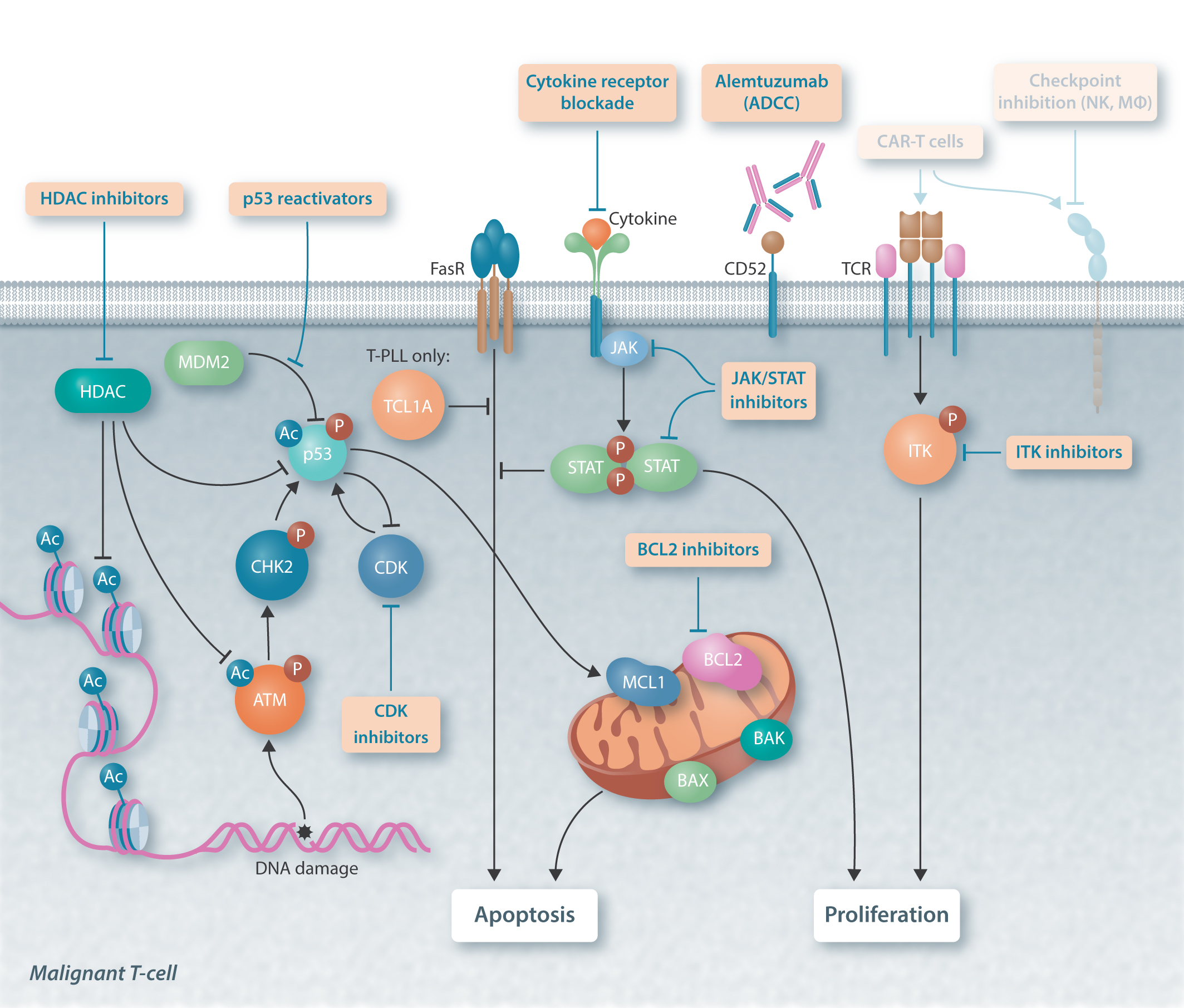
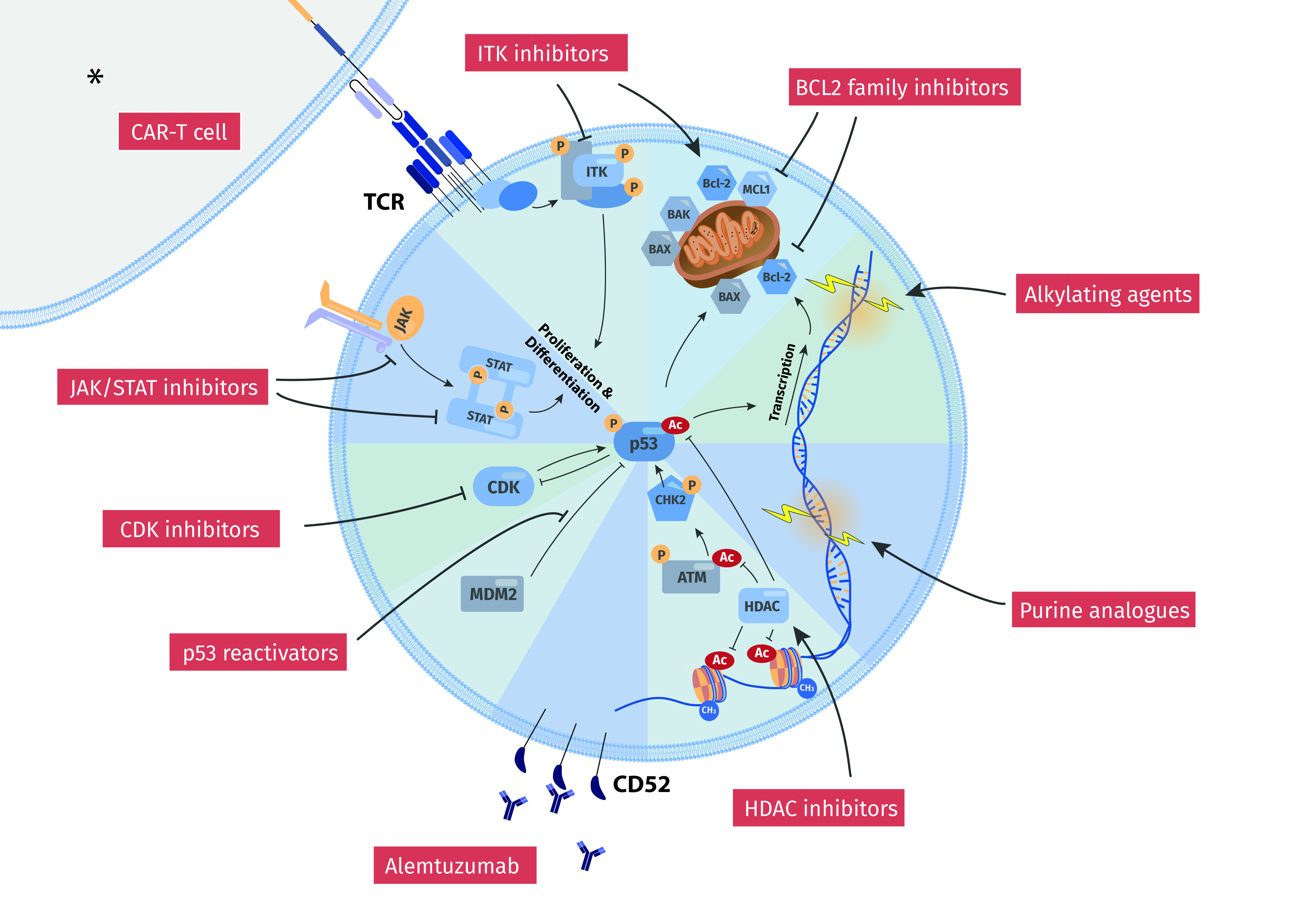
Although activation of the B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling pathway is implicated in the pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), its clinical impact and the molecular correlates of such response are not clearly defined. T-cell leukemia 1 (TCL1), the AKT modulator and proto-oncogene, is differentially expressed in CLL and linked to its pathogenesis based on CD5+ B-cell expansions arising in TCL1-transgenic mice. We studied here the association of TCL1 levels and its intracellular dynamics with the in vitro responses to BCR stimulation in 70 CLL cases. The growth kinetics after BCR engagement correlated strongly with the degree and timing of induced AKT phospho-activation. This signaling intensity was best predicted by TCL1 levels and the kinetics of TCL1-AKT corecruitment to BCR membrane activation complexes, which further included the kinases LYN, SYK, ZAP70, and PKC. High TCL1 levels were also strongly associated with aggressive disease features, such as advanced clinical stage, higher white blood cell counts, and shorter lymphocyte doubling time. Higher TCL1 levels independently predicted an inferior clinical outcome (ie, shorter progression-free survival, P < .001), regardless of therapy regimen, especially for ZAP70+ tumors. We propose TCL1 as a marker of the BCR-responsive CLL subset identifying poor prognostic cases where targeting BCR-associated kinases may be therapeutically useful.